lab techniques and accuracy in positioning pipettes|laboratory pipetting techniques : companies The position of the first stop is directly related to the volume setting. Set the pipette to 5μL and feel the position of the stops. Now set the pipette to 20μL and note the difference. At 20μL, the first stop is at the lowest position possible, since it is the maximum volume it can dispense. Using the software, starting, stopping and downloading data from the OM-CP-HITEMP140 is simple and easy. Graphical, tabular and summary data is provided for analysis and data can be viewed in °C, °F, K or °R. The data .Autoclave kills microorganisms using saturated stem under pressure. Autoclave comprises of three parts: a pressure chamber, a lid and an electrical heater.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Many use the terms autoclave and steam sterilization synonymously, but an autoclave applies to medical tools, and steam sterilization can apply to anything in need of sterilizing.
In this experiment 200µL of viscous liquid (glycerol) was pipetted 10 times by using both forward and reverse pipetting techniques. The pipette used was adjusted for glycerol using forward .
However, it’s important to note that electronic air displacement pipettes, while capable of dispensing partial volumes, lack the accuracy required for multi-dispensing. For such tasks, electronic repetitive pipettes, which are .
pipetting fluid accuracy
pipette accuracy
The position of the first stop is directly related to the volume setting. Set the pipette to 5μL and feel the position of the stops. Now set the pipette to 20μL and note the difference. At 20μL, the first stop is at the lowest position possible, since it is the maximum volume it can dispense.displacement pipettes. piston pipette tip How an air displacement pipette works? 1. The piston moves to the appropriate position when the volume is set. 2. When the operating button is pressed to the first stop, the piston expels the same volume of air as indicated on the volume setting. 3. After immersing the tip into the liquid, the operating . Accurately using graduated pipette use is crucial in any lab setting. This straightforward guide will take you through the essentials of graduated pipette use, from the correct technique to ensuring consistent measurements—without the fluff.. Graduated Pipette Use: Key Takeaways. Graduated pipette use is precision tools that come in various types . Guidelines are in place to ensure that the laboratory equipment is maintained and meets regulatory specifications for accuracy and precision, which are pre-requisites for laboratory certification .
Choosing the correct pipetting technique helps securing the accuracy and precision necessary for reproducible, reliable results. Especially when pipetting small volumes the influence of the pipetting technique can have tremendous effects on the experimental result. Two main techniques exist and each should be applied depending on the sample liquid.Store pipettes in an upright position when not in use. Pipette stands are ideal for this purpose. Check calibration regularly, depending on the frequency of use and on the application, but at least once a year. If used daily, a three-month interval is recommended. Follow the instructions for recalibration in the manufacturer s instruction manual. Even though pipettes are all members of the precision-instruments lab equipment group, their preciseness should not be taken for granted. A lot of the accuracy and measuring depends on each scientist’s individual skills. Pipetting may be the very last thing you worry about when you’re approaching that lab bench and starting your experiment.Pipetting the smallest possible volumes involves specialized instruments and techniques. A repeater pipette may be your best choice to repeat-dispense volumes down to 100 nL. Another pipette can also work for just a few dispenses. Make sure to use the smallest-size pipette that will accommodate the volume you wish to pipette.
Volume transfers with sterile solutions and cultures using instruments such as serological pipettes and micropipettors are one of many types of routine techniques done in a laboratory. Different experimental applications call for instruments capable of transferring distinct, yet precise and accurate, volumes.The serological pipette is frequently used in the laboratory for transferring milliliter volumes of liquid, from less than 1 ml to up to 50 ml. The pipettes can be sterile, plastic, and disposable or sterilizable, glass and reusable. Both kinds of pipettes use a pipet-aid, for the aspiration and dispensation of liquids.Learn the top 5 tips for maintaining and caring for your pipettes. Discover how proper cleaning, calibration, storage, handling, and maintenance can enhance accuracy and prolong the lifespan of your pipettes. Improve the quality of your experiments with these essential pipette care guidelines.
PRECISION AND ACCURACY Objectives 1. To become familiar with different types of laboratory glassware . our chemistry lab, both the 10-mL volumetric pipette and 50-mL volumetric flask are very precisely manufactured and have two significant figures after the decimal point (i.e. 10.00 mL and 50.00 mL). A beaker is less precisely manufactured; a . What is a micropipette? A micropipette is a laboratory instrument designed specifically for precise and accurate measurement and transfer of small volumes of liquid samples, typically in the microliter range (µl). While regular pipettes or glass pipettes are suitable for transferring larger volumes in milliliters, micropipettes are essential tools for laboratories .displacement pipettes. piston pipette tip How an air displacement pipette works? 1. The piston moves to the appropriate position when the volume is set. 2. When the operating button is pressed to the first stop, the piston expels the same volume of air as indicated on the volume setting. 3. After immersing the tip into the liquid, the operating .
A pipette is a laboratory tool for precisely measuring and transferring small quantities of liquid. It is a cylindrical glass or plastic tube with a narrow end for liquid transfer and a bulb or other mechanism for drawing the . Selection of the correct pipette can significantly impact performance. Proper pipetting technique is also critical to ensure reliable results—poor technique is detrimental to accuracy and precision and can result in experimental errors. Electronic pipettes with repetitive pipetting capabilities enable reliable sample preparation. ReferencesThese often require more specialized techniques and/or equipment to dispense in a standardized manner. . By making the change from mechanical to electronic pipettes, labs can improve the accuracy, precision, and reproducibility of results and boost efficiency, all of which combine to ensure reliable and streamlined scientific research .“Realistically, no lab has all the pipettes that a user might desire, but if a user takes a look at what tools are available in the lab and department, they might get a better idea of what existing pipettes to implement in an assay or of what pipettes they might want to purchase.” Related Article: Tips for Low-Volume Pipetting
laboratory pipetting techniques
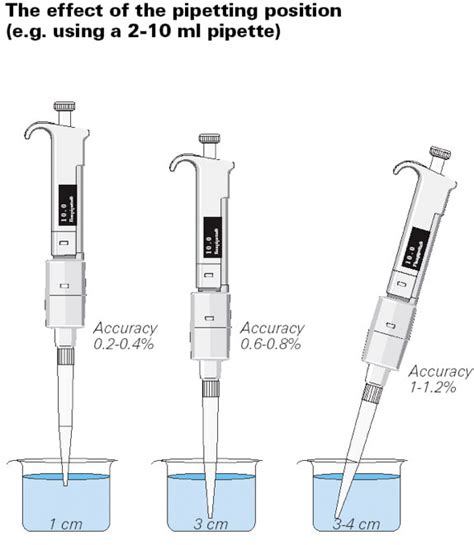
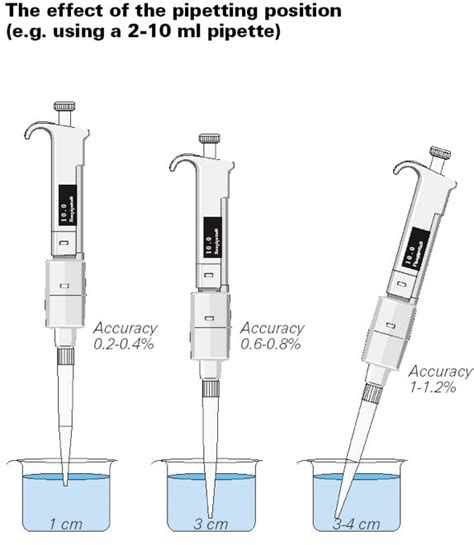
Place the end of the pipette straight into the opening on the pi-pump (green pi-pump for 5 and 10ml, blue pi-pump for 1m. Refer to Fig. 2 and Fig. 3l). Place the pipette tip into the solution; rotate the pi-pump wheel so that the fluid ascends. Slowly move the wheel so that you correctly deliver the required amount. Excessive immersion of the pipette tip is a very common source of error, and can increase inaccuracy up to 2-fold or more (0.6-0.8% inaccuracy compared to 0.2-0.4% inaccuracy when immersion depth is ideal). 1 This negative impact on accuracy is even more pronounced with very small sample volumes (ex. 1-10 µL) and in extreme cases, when the end .nominal volume pipette—even though it might be possible to pipette 100 µL with both. To illustrate this, Figure 1 shows two dispensing series of 100 µL ethanol, using an electronic Sartorius Picus® 50–1,000 µL pipette and a 5–120 µL pipette. With the Picus® 5–120 µL pipette, better accuracy The steps for measuring volumes using serological pipettes and micropipettors within a sterile field created by a Bunsen burner are presented, with the goal being for aseptic technique to become second nature when working at the bench. Microorganisms are everywhere - in the air, soil, and human body as well as on inanimate surfaces like laboratory benches and .
Manual pipetting is one of the most repetitive laboratory techniques. In a recent survey, more than 80% of life scientists reported pipetting for at least one hour every day, while almost 30% report pipetting for more than three hours. And the negative effects have a wide impact- manual pipetting has been associated with pain in 90% of users in one-hour uninterrupted pipetting sessions. In our lab, we most often pipette between 0.5 µl and 1000 µl, so I have developed three sets of training tips used with either the P1000, P200/20, or P10 pipette. . Pipetting accuracy can be assessed in a number of ways and will depend upon the students and lab infrastructure. To assess middle school and high school students, visual .
Laboratory Glassware: Determining the Density of Water Accuracy and Precision of Laboratory Glassware: Determining the Density of Water During the semester in the general chemistry lab, you will come into contact with various pieces of laboratory glassware. • beakers • Erlenmeyer Flasks • volumetric flasks • pipettes • burets
The accuracy of your test will improve if there is a slight difference between a pipette’s minimum volume and the volume being tested. For example, if you need to dispense 15 µL, a 1 mL pipette would be the wrong choice, whereas a 20 µL pipette would be ideal. 10. Use the correct pipette tip
laboratory pipetting system
lab pipetting practices pdf
how to improve pipette accuracy
how accurate is pipetting
The Tuttnauer line of large capacity autoclaves successfully meets the challenges posed by .
lab techniques and accuracy in positioning pipettes|laboratory pipetting techniques